Managing Diabetes: Tips for Leading a Healthy Life – A Step-by-Step Guide
Managing diabetes effectively is essential for maintaining your overall health and preventing complications. Whether you have type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes, leading a healthy lifestyle can make a significant difference in your quality of life. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to managing diabetes with clear, actionable steps.
Step 1: Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
Why It Matters:
Keeping track of your blood sugar levels helps you understand how food, activity, medication, and stress affect your glucose levels. Monitoring regularly allows you to take corrective actions to prevent spikes or dips in blood sugar.
Action Steps:
- Use a Glucometer: Get a reliable blood glucose meter and check your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider. Frequency may vary depending on your type of diabetes and treatment plan.
- Follow Your Target Ranges: Your doctor will give you specific blood sugar targets. For most people with diabetes, a typical range might be 80-130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL two hours after meals.
- Keep a Log: Record your blood sugar levels in a diary or app. Share this information with your healthcare provider during appointments to help adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
- Be Aware of Signs of High or Low Blood Sugar: Learn to recognize symptoms like fatigue, shakiness, dizziness, or confusion, which may indicate high (hyperglycemia) or low (hypoglycemia) blood sugar levels.

Step 2: Adopt a Balanced, Diabetes-Friendly Diet
Why It Matters:
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. Eating the right foods in the right amounts helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and provides your body with essential nutrients.
Action Steps:
- Focus on Complex Carbohydrates: Opt for whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits with low glycemic index (GI) levels. These carbohydrates are digested slowly, causing a gradual rise in blood sugar.
- Portion Control is Key: Even healthy foods can affect your blood sugar if eaten in large amounts. Use portion control strategies like measuring your food and using smaller plates.
- Include Lean Protein and Healthy Fats: Incorporate lean proteins (like chicken, fish, and beans) and heart-healthy fats (like olive oil, avocados, and nuts) in your meals to keep you full and reduce sugar cravings.
- Limit Sugary and Processed Foods: Avoid sugary drinks, candy, baked goods, and processed snacks that can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar.
- Eat Consistently: Try to eat at the same times each day and avoid skipping meals. Regular eating patterns help regulate blood sugar levels.
Step 3: Stay Physically Active
Why It Matters:
Exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently, allowing glucose to enter your cells and provide energy. Regular physical activity can also help you maintain a healthy weight, lower blood pressure, and improve your overall well-being.
Action Steps:
- Aim for 150 Minutes of Moderate Exercise Weekly: Try to engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise (like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming) five days a week.
- Incorporate Strength Training: Include two sessions of strength training per week, using weights or resistance bands. Building muscle helps your body use insulin better.
- Choose Activities You Enjoy: Whether it’s dancing, gardening, or walking the dog, find exercises that you enjoy so you’ll be more likely to stick with them.
- Monitor Your Blood Sugar During Exercise: Check your blood sugar before and after exercise, especially if you’re using insulin or other medications that affect glucose levels. Always carry a snack in case of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
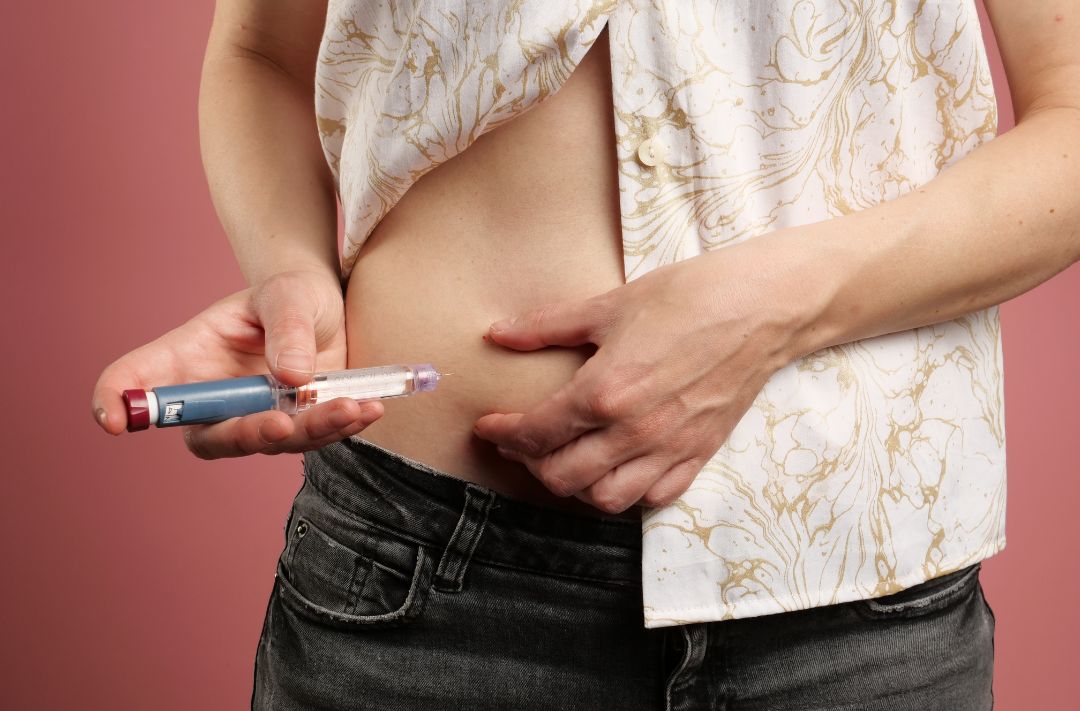
Step 4: Take Medications as Prescribed
Why It Matters:
For many people with diabetes, medication is necessary to manage blood sugar levels. Whether you’re on insulin, oral medications, or other treatments, it’s essential to take them as directed by your healthcare provider.
Action Steps:
- Follow Your Doctor’s Instructions: Take your medications at the correct times and dosages as prescribed. Skipping doses can lead to unstable blood sugar levels.
- Understand Your Medications: Know how each medication works, potential side effects, and how they interact with your diet or other medications. If you have questions, ask your healthcare provider for clarification.
- Adjust Based on Blood Sugar: Some medications, like insulin, may require adjustments based on your blood sugar readings. Make sure you know how and when to make these changes.
- Never Stop Medications Without Consulting Your Doctor: Even if you feel better, stopping your medications suddenly can cause your blood sugar to rise dangerously.
Step 5: Manage Stress Effectively
Why It Matters:
Stress can increase blood sugar levels due to the release of stress hormones like cortisol. Learning how to manage stress helps you keep your diabetes under control and improves your mental and physical health.
Action Steps:
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate activities like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga into your daily routine to help reduce stress levels.
- Stay Active to Combat Stress: Exercise not only benefits your physical health but also helps lower stress and anxiety. Even a short walk can help clear your mind and reduce stress.
- Get Plenty of Rest: Adequate sleep is essential for managing stress and blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night and establish a calming bedtime routine.
- Talk to a Counselor or Support Group: If you’re feeling overwhelmed, consider talking to a therapist or joining a diabetes support group. Sharing your challenges and learning from others can help relieve stress.

Step 6: Maintain a Healthy Weight
Why It Matters:
Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can make it harder for your body to use insulin effectively, leading to higher blood sugar levels. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight helps improve insulin sensitivity and reduce diabetes-related complications.
Action Steps:
- Set Realistic Weight Loss Goals: If you’re overweight, aim to lose 5-10% of your body weight, which can significantly improve blood sugar levels.
- Follow a Balanced Diet: Focus on portion control and nutrient-dense foods that support weight loss, like whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise, combined with a healthy diet, is key to successful weight loss. Find activities you enjoy to make staying active sustainable.
- Track Your Progress: Use a journal or app to track your weight loss, food intake, and exercise habits. Celebrate small victories along the way to stay motivated.
Step 7: Get Regular Health Checkups
Why It Matters:
Routine medical appointments are essential for monitoring your diabetes and preventing complications such as heart disease, nerve damage, or vision problems.
Action Steps:
- Visit Your Doctor Regularly: Schedule appointments with your healthcare provider every 3 to 6 months to monitor your blood sugar control, medications, and overall health.
- Get Your A1C Test: This blood test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. Aim for an A1C level below 7% (or as recommended by your doctor).
- Monitor Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: People with diabetes are at higher risk for heart disease, so regular monitoring of your blood pressure and cholesterol levels is crucial.
- Check Your Eyes and Feet: Schedule yearly eye exams to check for diabetic retinopathy (damage to the blood vessels in your eyes) and regularly inspect your feet for cuts or sores that could lead to infections.
Step 8: Be Prepared for Emergencies
Why It Matters:
Managing diabetes can sometimes lead to sudden changes in blood sugar levels that require immediate attention. Being prepared for emergencies helps you manage these situations effectively.
Action Steps:
- Carry Fast-Acting Sugar: Always have a source of fast-acting glucose, such as glucose tablets or juice, on hand in case of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
- Wear Medical ID: Consider wearing a medical ID bracelet or carrying a diabetes identification card so that others can assist you in an emergency.
- Have an Emergency Plan: Discuss with your healthcare provider what to do in case of severe hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Make sure friends, family, or coworkers know how to help if needed.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes requires a combination of healthy habits, regular monitoring, and consistent communication with your healthcare provider. By adopting these steps—monitoring blood sugar, eating a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress—you can lead a healthy life and prevent diabetes-related complications. At Puracare Specialist Hospital, we provide comprehensive diabetes care, from education and support to regular health checkups. Let us help you manage your diabetes for a healthier, happier life.